
- Pretreatment Section of the Oil Mill Plant
- Pressing Section for Oil Mill Plant
- Solvent Extraction Plant
- Oil Refining Plant
- Filling Section of the Oil Mill Plant
- Oil Modification Plant
- Seed Processing Plant
- Small Oil Production Line
- oil press
- YZS-30 Sesame Oil Pressing Machine
- YZS-68 Soya Oil Press
- YZS-80 Canola Oil Press
- YZS-95 Sunflower Seed Oil Press
- YZS-100 Oil Expeller Press
- YZS-120 Oil Pressing Machinery
- YZS-130 Screw Oil Press
- YZS-160 Oil Seed Press
- YZS-80A Combined Oil Press
- YZS-95A Automatic Oil Press Machine
- YZS-100A Automatic Oil Expeller
- Steel Silo
- Face Mask
- Oil Production Process 5S Groundnut
- Physical Refining Process Of The Edible Oil Refining Machine
- Cottonseed Oil Processing Equipment
- Something About Sunflower Oil Extraction Machine
- Something About Soybean Oil Refining Machine
- Something About Edible Oil Solvent Extraction
- Rice Bran Oil Extraction Equipment
- Soybean Oil Refining Equipment
vegetable oil processing
Vegetable Oil Processing
Vegetable oil processing is a complicated oil processing process. For different oil seeds the production process is diffent too.
Vegetable oils are being processed by grinding, cooking, expelling and pressing, or by solvent extraction of the raw materials. The process for soybeans typically consists of five steps: oilseed handling / elevator operations, preparation of soybeans for solvent extraction, solvent extraction and oil desolventizing, flake desolventizing, and oil refining. Corn, cottonseed, and peanut oil and other oilseeds vegetable oil processing are similar to soybean oil processing, except for differences in the soybean preparation for oil extraction.
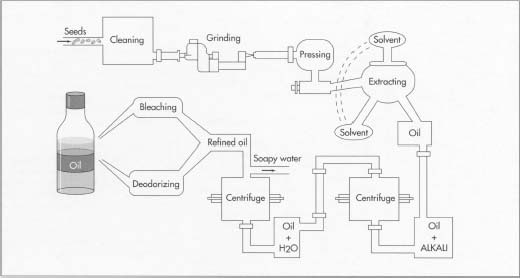
Detailed Vegetable Oil Processing Steps

Vegetable Oil Processing - Seed Preparation
Vegetable oil seeds are conveyed from the process bins to the mill by means of belts or mass flow conveyors and bucket elevators. The cracking rolls crack each bean into four to six particles, which are passed through aspirators to remove the hulls (processed separately after the removal of residual bean chips). These hulls may be combined with the hulls from the grain cleaning step. Next, the cracked beans and bean chips are conveyed to the conditioning area, where they are put either into a rotary steam tubed device or into a stacked cooker and are heated to condition them.
Vegetable Oil Processing - Solvent Extraction and Oil Desolventizing
The extraction process consists of washing the oil from the soybean flakes with hexane solvent in a countercurrent extractor. Then the solvent is evaporated (i. e., desolventized) from both the solvent/oil mixture (micella) and the solvent-laden, defatted flakes. The oil is desolventized by exposing the solvent/oil mixture to steam (contact and noncontact). Then the solvent
is condensed, separated from the steam condensate, and reused. Residual hexane not condensed is removed with mineral oil scrubbers. The desolventized oil, called crude soybean oil, is stored for further processing or loadout.
Vegetable Oil Processing - Oil Refining
Crude oil is typically shipped for refining to establishments engaged in the production of edible vegetable oils, shortening, and margarine. Crude vegetable oils contain small amounts of naturally occurring materials such as proteinaceous material, free fatty acids, and phosphatides. Phosphatides are removed for lecithin recovery or to prepare the crude oil for export. The most common method of refining oil is by reacting it with an alkali solution which neutralizes the free fatty acids and reacts with the phosphatides.
Whenever you would like to start a vegetable oil processing business, don't forget to contact us, we are always at your service!


